A. In the following figure θ C is called contact angle, which is a measure of the degree of wetting.
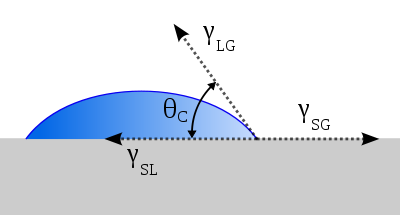
Definition: Contact angle refers to the angle between the tangent line of the gas-liquid interface at the intersection of gas, liquid, and solid, passing through the boundary between the liquid and the solid-liquid interface θ C.
1) When θ C < 5 °~10 °, basic wetting, super hydrophilic;
2) When θ C<90 °, partially wet or wet, and the smaller the value, the better the wettability, indicating hydrophilicity;
3) When θ C=90 °, which is the boundary between wetting and non wetting;
4) When θ C > 90 °, non wetting, liquid surface shrinks into a hemispherical shape, indicating hydrophobicity.
5) When θ C > 150 °, completely non wetting, the liquid surface shrinks into a spherical shape, which is superhydrophobic.
B. The state in the figure below is called hydrophilic.
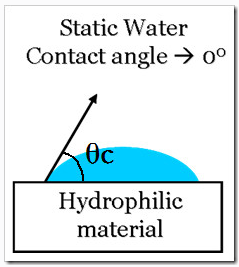
Zixi Lai is super hydrophilic and has a contact angle θ C approaches 5 °

C. The state in the figure below is called Hydrophobic.
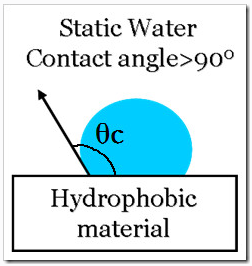
Zixilai WNS superhydrophobic coating, contact angle θ C>150 ° is called superhydrophobicity.

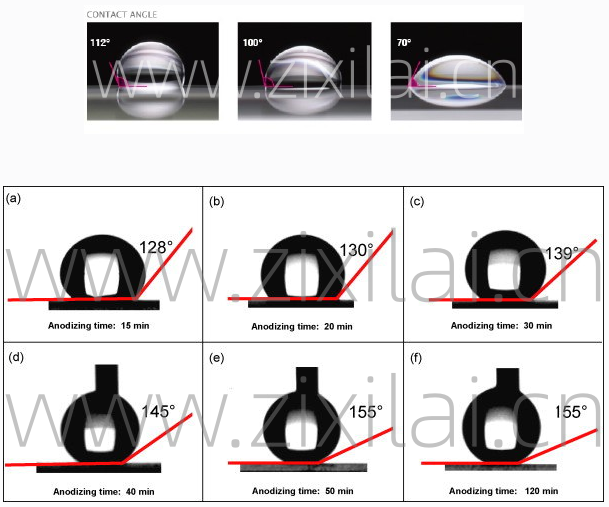
In order to have a more direct impression, here are some examples of contact angles: